Curious about how a plant-based diet can revolutionize your health? Going vegan isn’t just about cutting out animal products; it’s about opening your kitchen to a diverse world of vibrant, nutrient-packed foods that nourish your body and mind. Whether you’re considering veganism for its ethical values, environmental benefits, or potential health improvements, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know to make the transition seamless and exciting.
A vegan diet replaces all animal-derived products with plant-based alternatives, offering a colorful variety of fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds. Not only can these foods provide the essential nutrients you need, but they can also help you discover new flavors and creative ways to enjoy meals. Let’s explore how a well-planned vegan diet can meet your nutritional needs while making a positive impact on your health and lifestyle.
What Does a Vegan Diet Include?
Veganism opens the door to an abundance of plant-based foods that can transform your diet:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Think colorful plates loaded with fresh produce like spinach, kale, berries, and broccoli, packed with vitamins and antioxidants.
- Whole Grains: Quinoa, brown rice, oats, and millet provide complex carbs, fiber, and essential nutrients.
- Legumes and Pulses: Lentils, chickpeas, black beans, and split peas are excellent sources of protein and fiber.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, chia seeds, flaxseeds, and sunflower seeds offer healthy fats, protein, and important minerals.
- Plant-Based Proteins: Tofu, tempeh, seitan, and plant-based meats serve as protein-rich alternatives.
Foods to Avoid
On a vegan diet, you’ll need to avoid all animal products, which include:
- Meat and poultry
- Fish and seafood
- Dairy products
- Eggs
- Honey
Key Nutritional Considerations
Switching to a vegan diet requires a bit of attention to ensure you’re getting all the necessary nutrients. Here’s a quick look at some key areas to focus on:
- Vitamin B12: Since this vitamin is found in animal products, you’ll need to incorporate B12-fortified foods or take a supplement.
- Iron: Plant-based iron is found in foods like lentils, beans, and fortified cereals. Pairing them with vitamin C-rich foods can boost absorption.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Look for fortified plant milks and juices, or consider a supplement to support bone health.
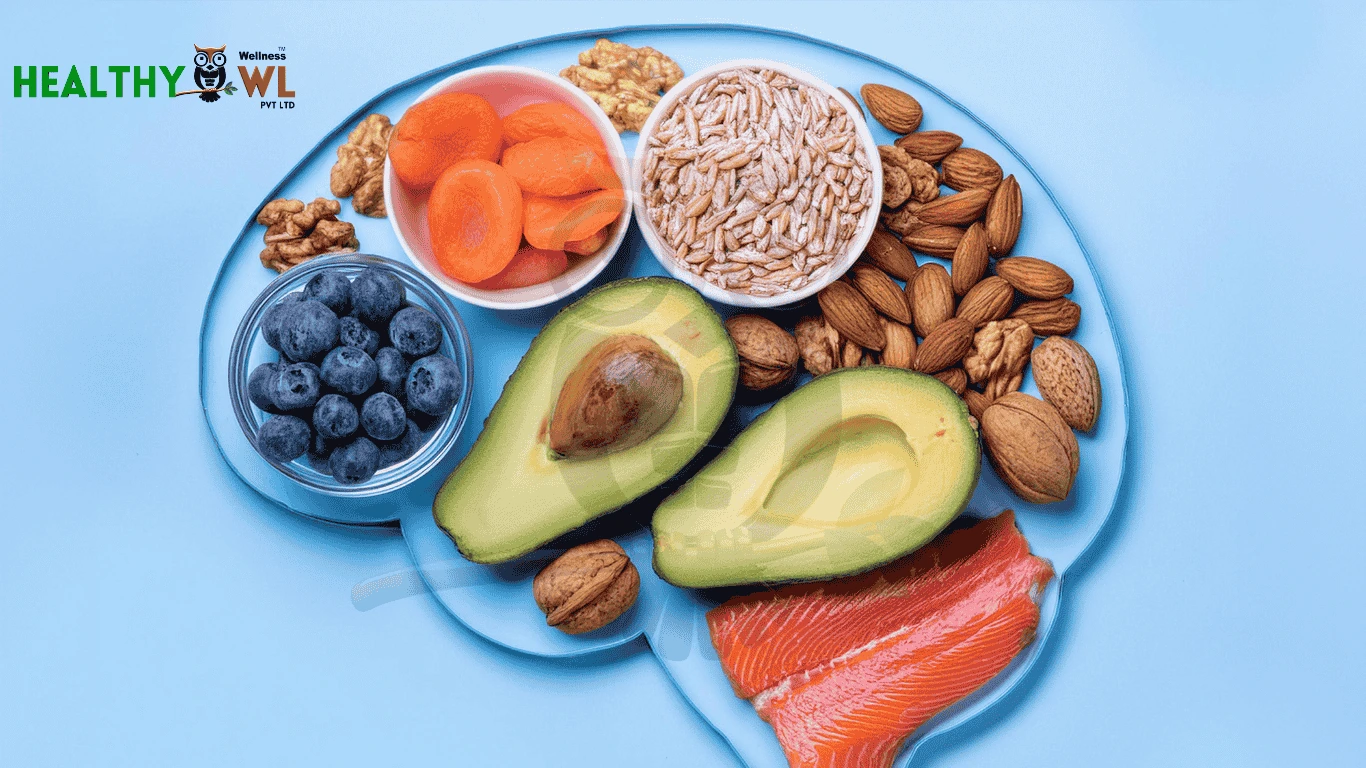
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts are rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), but you might also benefit from an algae-based omega-3 supplement.
- Protein Intake: While legumes, nuts, and plant-based proteins like tofu and tempeh provide good protein, combining certain plant proteins (like beans and grains) ensures a complete amino acid profile, especially for those new to veganism.
- Zinc: This nutrient can be lower in vegan diets, so include zinc-rich foods like pumpkin seeds, chickpeas, and lentils.
- Iodine: Primarily found in dairy and seafood, iodine intake should be considered. Seaweed and iodized salt can help meet the requirement.
- Selenium: Brazil nuts are a great source of selenium, which may be limited in some plant-based diets. Just one or two nuts a day can meet the daily requirement.
Reading Labels for Hidden Ingredients
Be mindful that some packaged foods, even those that seem plant-based, might contain animal-derived ingredients like gelatin, casein, or whey. Reading labels is key to ensuring your food aligns with your vegan lifestyle.
The Benefits of a Vegan Diet
- Weight Management: Many studies have shown that vegans tend to have lower body weights, partly due to the higher intake of fiber-rich, lower-calorie foods.
- Heart Health: Plant-based diets are known for improving heart health by lowering cholesterol levels and blood pressure.
- Better Blood Sugar Control: A vegan diet rich in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables can help stabilize blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Lower Disease Risk: Studies suggest that a well-balanced vegan diet may reduce the risk of certain cancers, hypertension, and chronic diseases.
Transition Tips
Making the shift to a vegan diet can be exciting. Here are some practical tips for transitioning:
- Gradually replace animal products with plant-based alternatives.
- Consider meal prepping to ensure balance throughout your day, making it easier to maintain a nutritious vegan diet.
By exploring veganism, you’ll not only enhance your health but also expand your culinary horizons. From creamy plant-based yogurts to protein-packed lentil dishes, the possibilities are endless. Dive into the world of veganism and discover how delicious and nutritious plant-based living can truly be.
Follow this easy recipe to make a delicious vegan yogurt for you:
Easy Vegan Coconut Yogurt Recipe
Interested in starting your vegan journey?
Reach out to us for personalized guidance on transitioning to a plant-based diet!
Sources: